Assistant Professor, Section of Computational Biomedicine, Department of Medicine, BUSM
Joshua Campbell received his Bachelor’s degree from Anderson University with degrees in Biology, Computer Science, and Mathematics. He earned a Ph.D. in Bioinformatics from Boston University in the lab of Avrum Spira and Marc Lenburg to identify mechanisms of COPD pathogenesis. He then performed his postdoctoral research at Dana-Farber Cancer Institute and the Broad Institute of Harvard and MIT with Matthew Meyerson where he worked with The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) to identify novel mutational drivers of lung cancer. He is currently an assistant professor in the Department of Medicine at Boston University School of Medicine (BUSM) where he develops novel Bayesian approaches to analyze genomic data in the setting of cancer. He is also the co-scientific director of the BU Medical Campus Single Cell Sequencing core.
Email: camp@bu.edu
Outside links:
BU Profile CBM Profile Google Scholar LinkedIn GithubPublications

Characterization of highly active mutational signatures in tumors from a large Chinese population
Abstract The majority of mutational signatures have been characterized in tumors from Western countries and the degree to which mutational signatures are similar or different in Eastern populations has not been fully explored. We leveraged a large-scale clinical sequencing cohort of tumors from a Chinese population containing 25 tumor types and found that the highly ……

Characterization and decontamination of background noise in droplet-based single-cell protein expression data with DecontPro
Assays such as CITE-seq can measure the abundance of cell surface proteins on individual cells using antibody derived tags (ADTs). However, many ADTs have high levels of background noise that can obfuscate down-stream analyses. Using an exploratory analysis of PBMC datasets, we find that some droplets that were originally called “empty” due to low levels ……

Matrix and analysis metadata standards (MAMS) to facilitate harmonization and reproducibility of single-cell data
A large number of genomic and imaging datasets are being produced by consortia that seek to characterize healthy and disease tissues at single-cell resolution. While much effort has been devoted to capturing information related to biospecimen information and experimental procedures, the metadata standards that describe data matrices and the analysis workflows that produced them are ……

Integrative genetic and genomic networks identify microRNA associated with COPD and ILD
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and interstitial lung disease (ILD) are clinically and molecularly heterogeneous diseases. We utilized clustering and integrative network analyses to elucidate roles for microRNAs (miRNAs) and miRNA isoforms (isomiRs) in COPD and ILD pathogenesis. Short RNA sequencing was performed on 351 lung tissue samples of COPD (n=145), ILD (n=144) and controls ……

Interactive analysis of single-cell data using flexible workflows with SCTK2.0
Analysis of single-cell RNA-seq (scRNA-seq) data can reveal novel insights into heterogeneity of complex biological systems. Many tools and workflows have been developed to perform different types of analysis. However, these tools are spread across different packages or programming environments, rely on different underlying data structures, and can only be utilized by people with knowledge ……
A single-cell lung atlas of complement genes identifies the mesothelium and epithelium as prominent sources of extrahepatic complement proteins
To understand functional duality of the complement system in host defense and lung injury, a more comprehensive view of its localized production in the lung, and the impact of age on complement production are essential. Here, we explored the expression of complement genes through computational analysis of preexisting single cell RNA sequencing data from lung ……
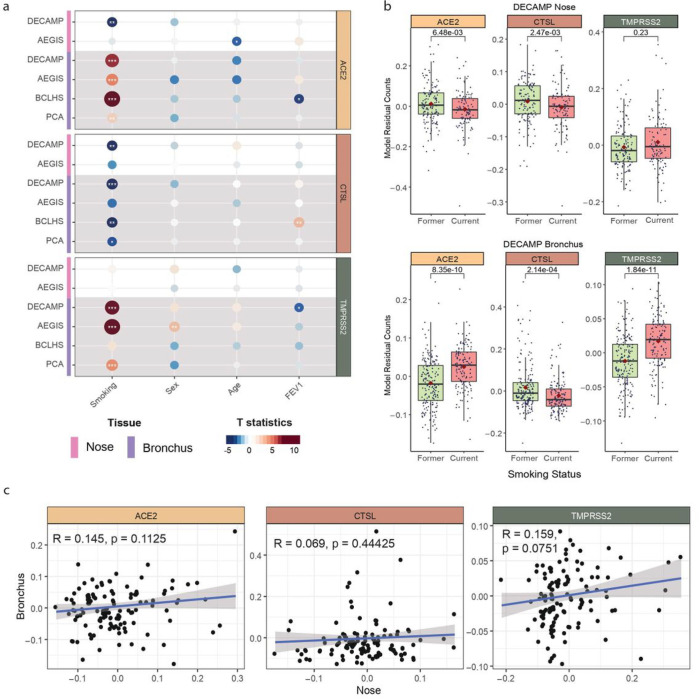
Smoking Modulates Different Secretory Subpopulations Expressing SARS-CoV-2 Entry Genes in the Nasal and Bronchial Airways
Xu, K., Shi, X., Husted, C., Hong, R., Wang, Y., Ning, B., Sullivan, T., Rieger-Christ, K., Duan, F., Marques, H., Gower, A., Xiao, X., Liu, H., Liu, G., Duclos, G., Platt, M., Spira, A., Mazzilli, S., Billatos, E., Lenburg, M., … Beane, J. (accepted by scientific report) Abstract Background: SARS-CoV-2 infection and disease severity are ……
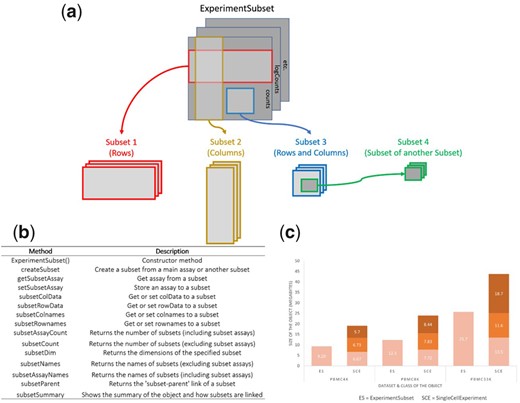
ExperimentSubset: an R package to manage subsets of Bioconductor Experiment objects
Motivation R Experiment objects such as the SummarizedExperiment or SingleCellExperiment are data containers for storing one or more matrix-like assays along with associated row and column data. These objects have been used to facilitate the storage and analysis of high-throughput genomic data generated from technologies such as single-cell RNA sequencing. One common computational task in many genomics analysis workflows ……
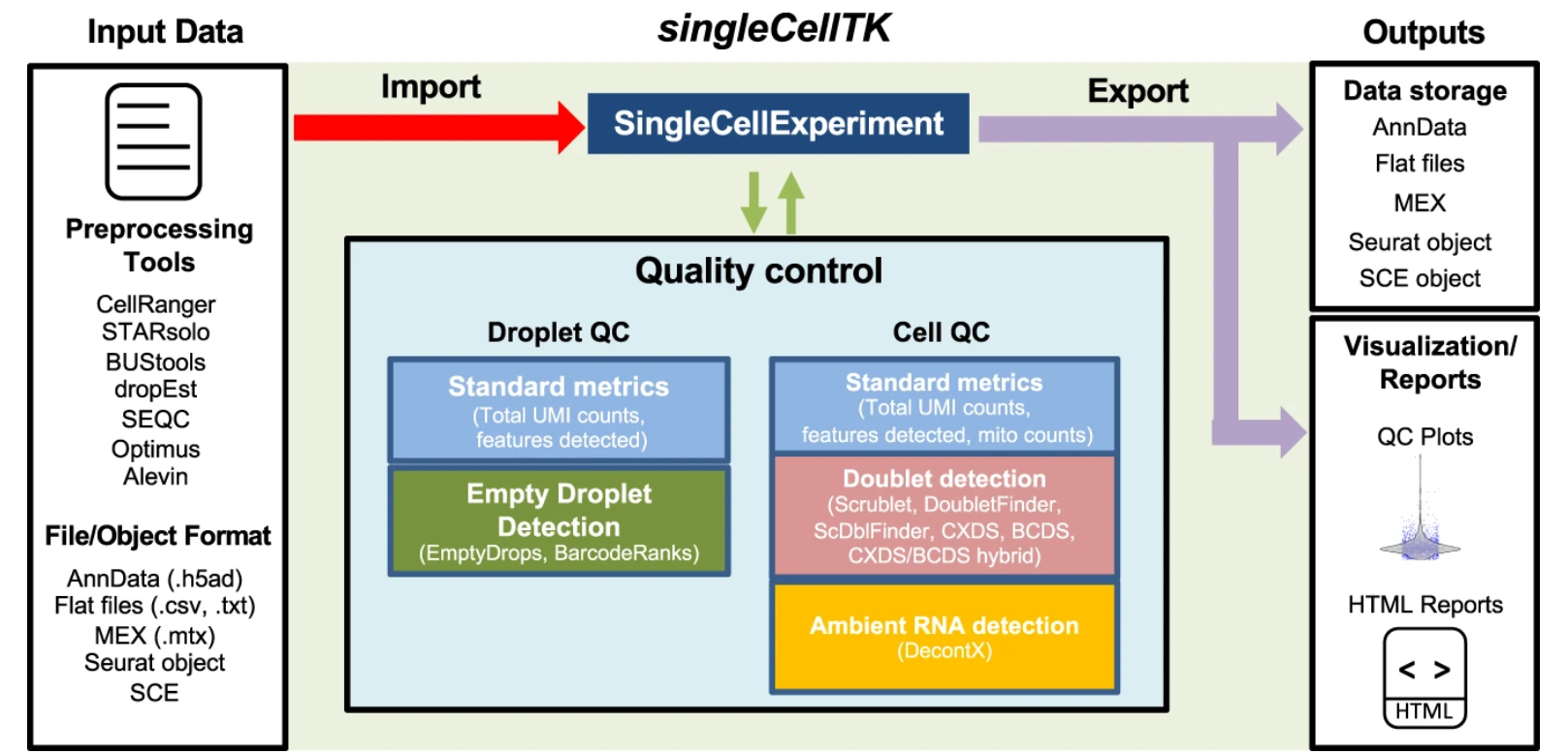
Comprehensive generation, visualization, and reporting of quality control metrics for single-cell RNA sequencing data
Single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) can be used to gain insights into cellular heterogeneity within complex tissues. However, various technical artifacts can be present in scRNA-seq data and should be assessed before performing downstream analyses. While several tools have been developed to perform individual quality control (QC) tasks, they are scattered in different packages across several ……
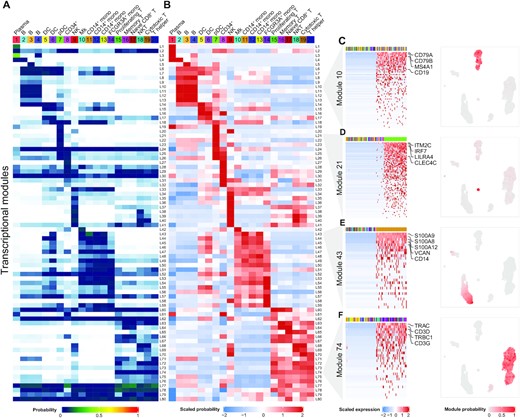
Celda: a Bayesian model to perform co-clustering of genes into modules and cells into subpopulations using single-cell RNA-seq data
Single-cell RNA-seq (scRNA-seq) has emerged as a powerful technique to quantify gene expression in individual cells and to elucidate the molecular and cellular building blocks of complex tissues. We developed a novel Bayesian hierarchical model called Cellular Latent Dirichlet Allocation (Celda) to perform co-clustering of genes into transcriptional modules and cells into subpopulations. Celda can ……
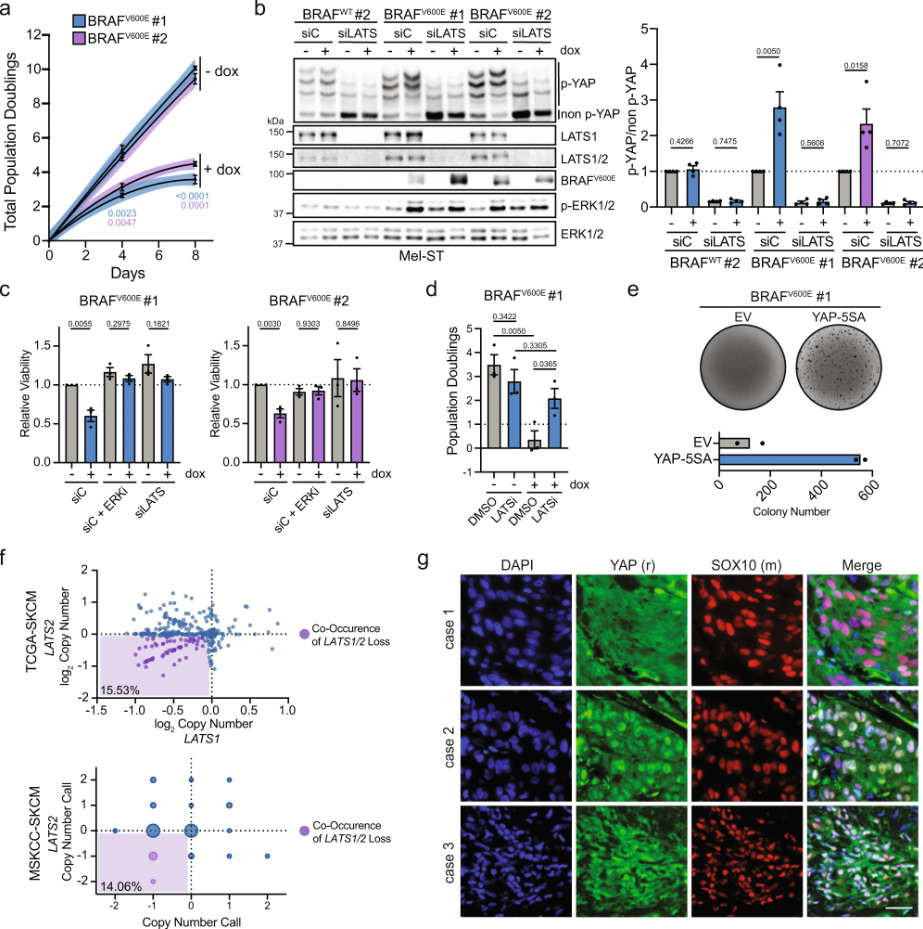
Inactivation of the Hippo tumor suppressor pathway promotes melanoma
Melanoma is commonly driven by activating mutations in the MAP kinase BRAF; however, oncogenic BRAF alone is insufficient to promote melanomagenesis. Instead, its expression induces a transient proliferative burst that ultimately ceases with the development of benign nevi comprised of growth-arrested melanocytes. The tumor suppressive mechanisms that restrain nevus melanocyte proliferation remain poorly understood. Here ……
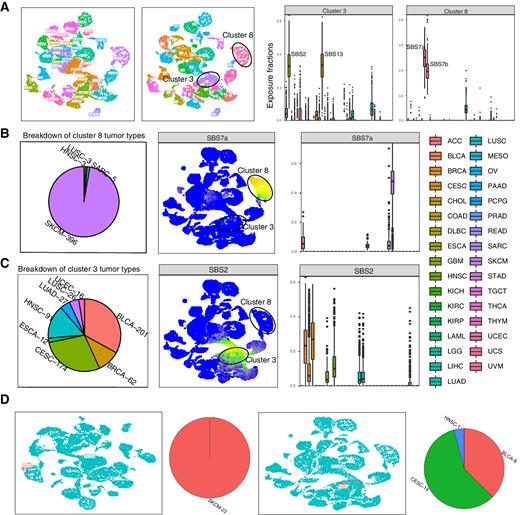
The Mutational Signature Comprehensive Analysis Toolkit (musicatk) for the Discovery, Prediction, and Exploration of Mutational Signatures
Mutational signatures are patterns of somatic alterations in the genome caused by carcinogenic exposures or aberrant cellular processes. To provide a comprehensive workflow for preprocessing, analysis, and visualization of mutational signatures, we created the Mutational Signature Comprehensive Analysis Toolkit (musicatk) package. musicatk enables users to select different schemas for counting mutation types and to easily ……

Whole-genome doubling confers unique genetic vulnerabilities on tumour cells
Ryan J. Quinton, Amanda DiDomizio, Marc A. Vittoria, Kristýna Kotýnková, Carlos J. Ticas, Sheena Patel, Yusuke Koga, Jasmine Vakhshoorzadeh, Nicole Hermance, Taruho S. Kuroda, Neha Parulekar, Alison M. Taylor, Amity L. Manning, Joshua D. Campbell & Neil J. Ganem Nature volume 590, pages492–497 (2021)Cite this article Abstract Whole-genome doubling (WGD) is common in human cancers, occurring early in tumorigenesis and generating genetically unstable tetraploid cells that fuel tumour development1,2. Cells that undergo WGD ……
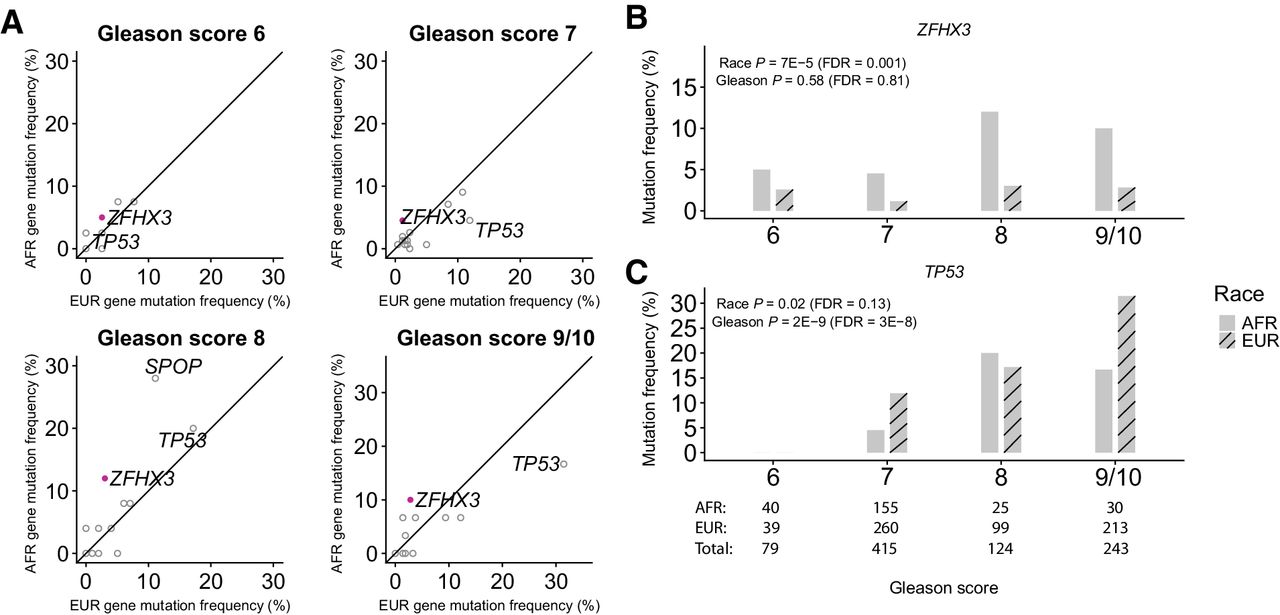
Genomic Profiling of Prostate Cancers from Men with African and European Ancestry
Yusuke Koga, Hanbing Song, Zachary R. Chalmers, Justin Newberg, Eejung Kim, Jian Carrot-Zhang, Daphnee Piou, Paz Polak, Sarki A. Abdulkadir, Elad Ziv, Matthew Meyerson, Garrett M. Frampton, Joshua D. Campbell and Franklin W. Huang. Abstract Purpose: African American (AFR) men have the highest mortality rate from prostate cancer (PCa) compared with men of other racial/ancestral groups. Differences in the spectrum of somatic genome alterations in tumors between AFR men and other populations have not been well-characterized due to a lack of inclusion of significant ……

Decontamination of ambient RNA in single-cell RNA-seq with DecontX
Shiyi Yang, Sean E. Corbett, Yusuke Koga, Zhe Wang, W. Evan Johnson, Masanao Yajima, Joshua D. Campbell. Abstract Droplet-based microfluidic devices have become widely used to perform single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq). However, ambient RNA present in the cell suspension can be aberrantly counted along with a cell’s native mRNA and result in cross-contamination of transcripts between different ……
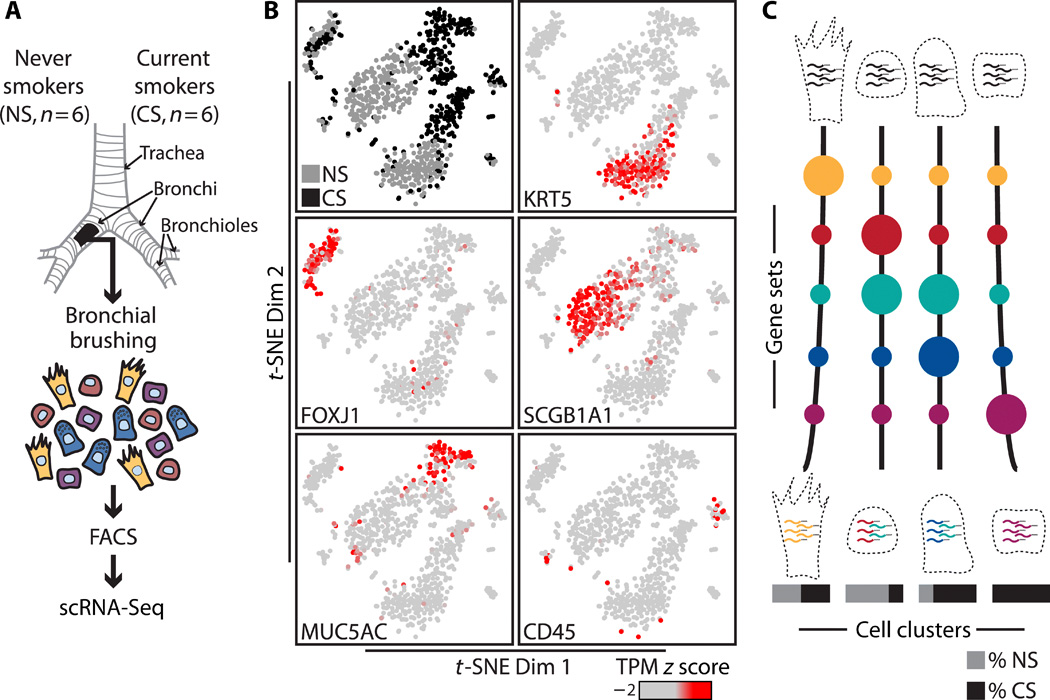
Characterizing smoking-induced transcriptional heterogeneity in the human bronchial epithelium at single-cell resolution
Grant E. Duclos, Vitor H. Teixeira, Patrick Autissier, Yaron B. Gesthalter, Marjan A. Reinders-Luinge, Robert Terrano, Yves M. Dumas, Gang Liu, Sarah A. Mazzilli, Corry-Anke Brandsma, Maarten van den Berge, Sam M. Janes, Wim Timens, Marc E. Lenburg, Avrum Spira, Joshua D. Campbell*, Jennifer Beane* Abstract The advent of high-throughput sequencing technologies has led to the ……

Pipeliner: A Nextflow-Based Framework for the Definition of Sequencing Data Processing Pipelines
Anthony Federico, Tanya Karagiannis, Kritika Karri, Dileep Kishore, Yusuke Koga, Joshua D. Campbell, Stefano Monti. Abstract The advent of high-throughput sequencing technologies has led to the need for flexible and user-friendly data preprocessing platforms. The Pipeliner framework provides an out-of-the-box solution for processing various types of sequencing data. It combines the Nextflow scripting language and Anaconda package ……
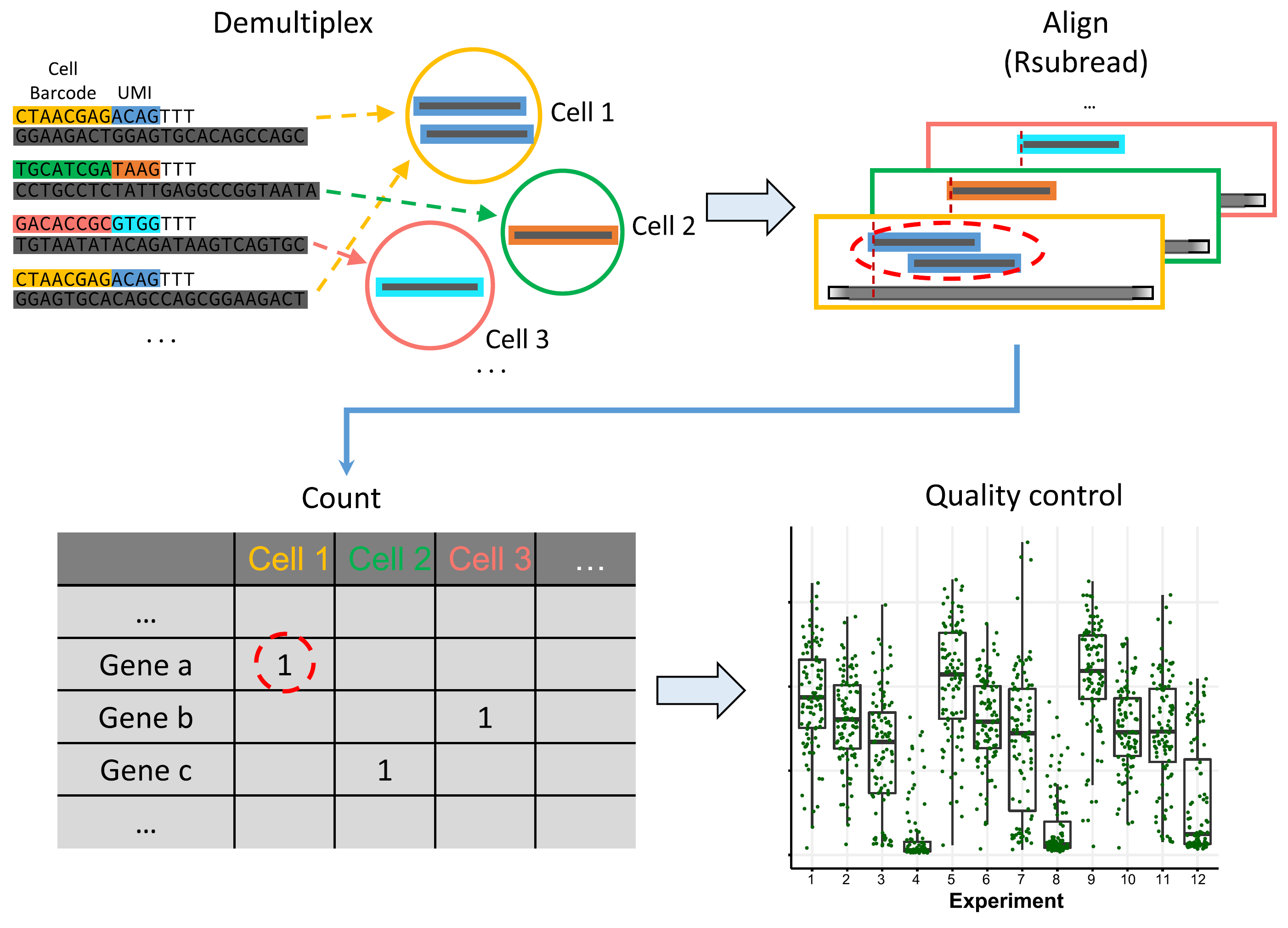
scruff: an R/Bioconductor package for preprocessing single-cell RNA-sequencing data
Zhe Wang, Junming Hu, W. Evan Johnson, Joshua D. Campbell Abstract Background: Single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) enables the high-throughput quantification of transcriptional profiles in single cells. In contrast to bulk RNA-seq, additional preprocessing steps such as cell barcode identification or unique molecular identifier (UMI) deconvolution are necessary for preprocessing of data from single cell protocols. R packages that ……
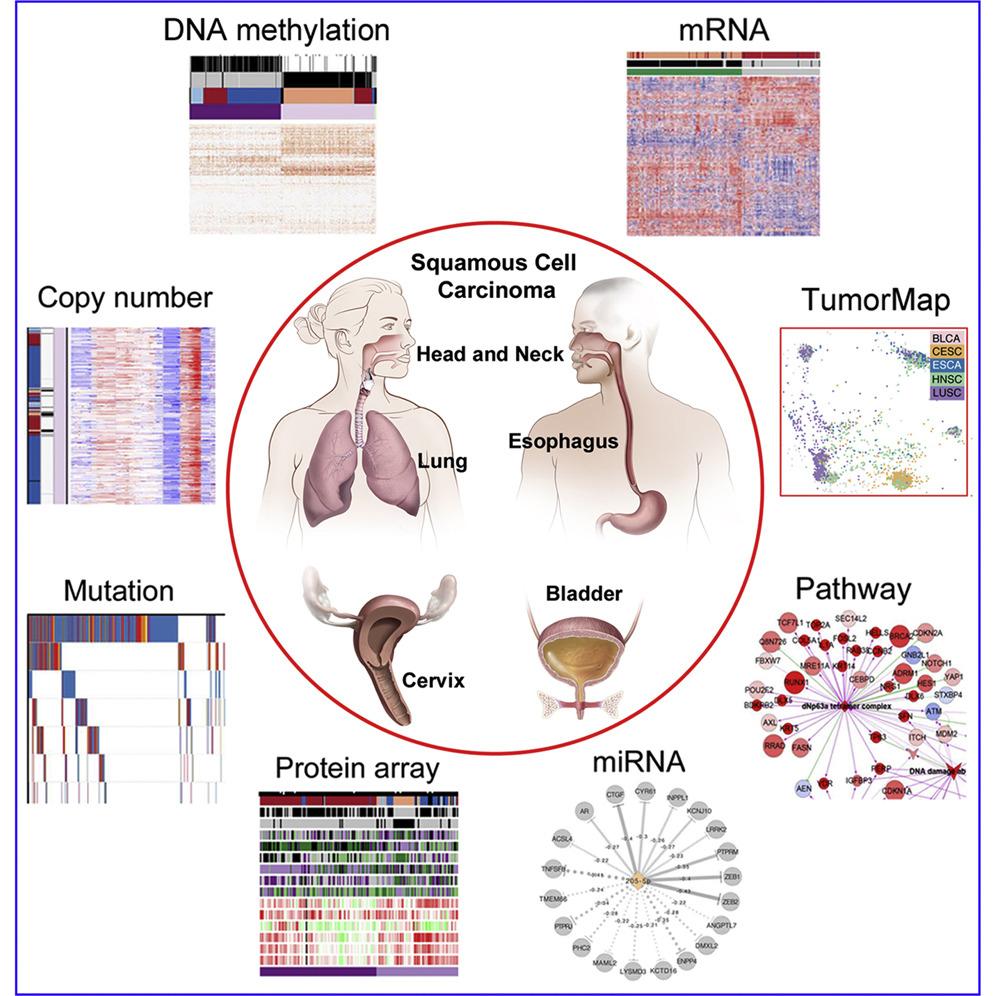
Genomic, Pathway Network, and Immunologic Features Distinguishing Squamous Carcinomas
Joshua D. Campbell, Christina Yau, Reanne Bowlby, Yuexin Liu, Kevin Brennan, Huihui Fan, Alison M. Taylor, Chen Wang, Vonn Walter, Rehan Akbani, Lauren Averett Byers, Chad J. Creighton, Cristian Coarfa, Juliann Shih, Andrew D. Cherniack, livier Gevaert, Marcos Prunello, Hui Shen, Pavana Anur, Jianhong Chen, Hui Cheng, D. Neil Hayes, Susan Bullman, Chandra Sekhar Pedamallu, ……
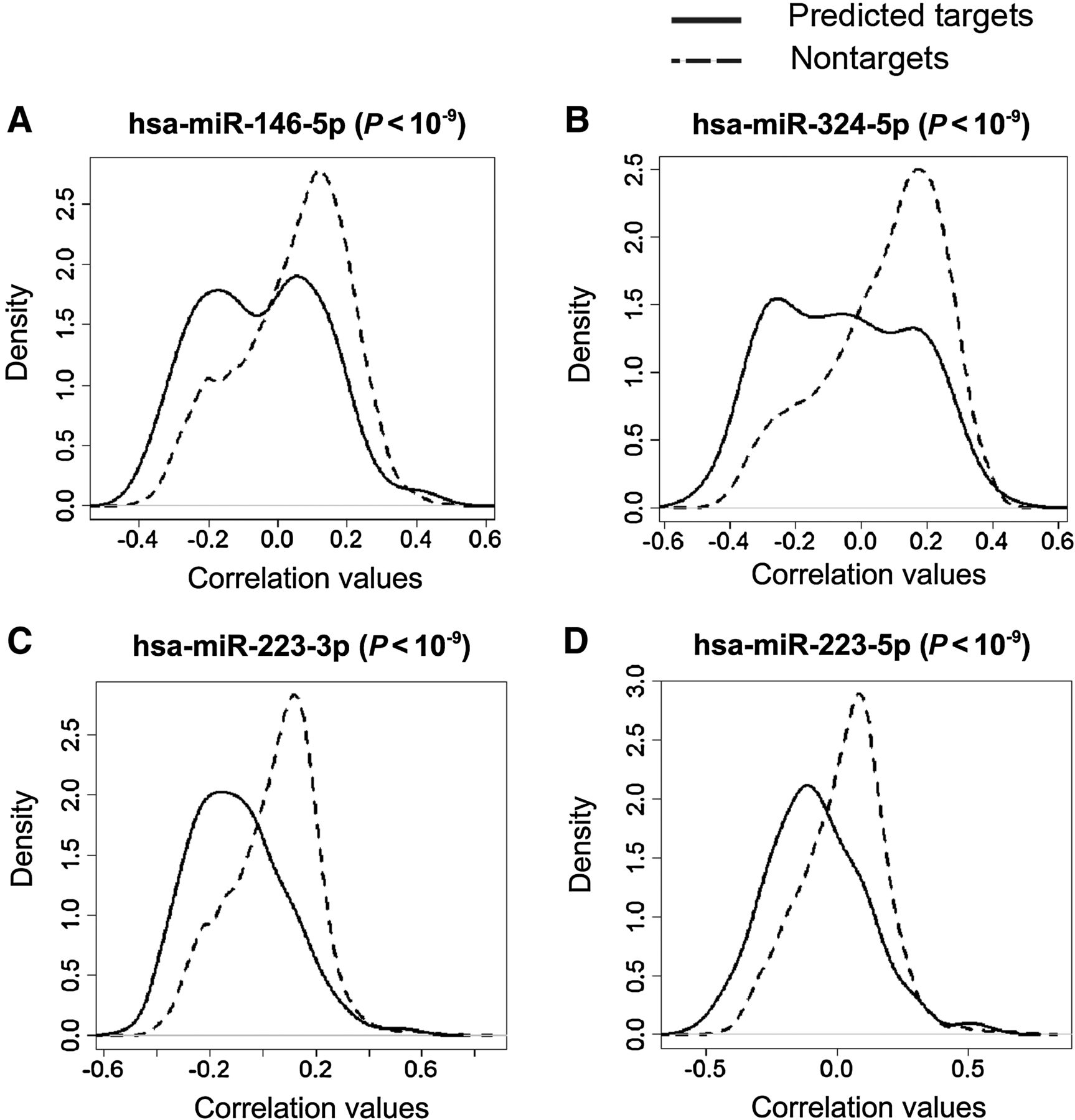
Alterations in Bronchial Airway miRNA Expression for Lung Cancer Detection
Ana B. Pavel, Joshua D. Campbell, Gang Liu, David Elashoff, Steven Dubinett, Kate Smith, Duncan Whitney, Marc E. Lenburg and Avrum Spira. Abstract We have previously shown that gene expression alterations in normal-appearing bronchial epithelial cells can serve as a lung cancer detection biomarker in smokers. Given that miRNAs regulate airway gene expression responses to smoking, ……

